Use Paddle-TensorRT Library for inference¶
NVIDIA TensorRT is a is a platform for high-performance deep learning inference. It delivers low latency and high throughput for deep learning inference application. Subgraph is used in PaddlePaddle to preliminarily integrate TensorRT, which enables TensorRT module to enhance inference performance of paddle models. The module is still under development. Currently supported models are AlexNet, MobileNet, ResNet50, VGG19, ResNext, Se-ReNext, GoogleNet, DPN, ICNET, Deeplabv3 Mobile, Net-SSD and so on. We will introduce the obtaining, usage and theory of Paddle-TensorRT library in this documentation.
Contents¶
[compile Paddle-TRT inference libraries](#compile Paddle-TRT inference libraries)
[Paddle-TRT interface usage](#Paddle-TRT interface usage)
[Paddle-TRT example compiling test](#Paddle-TRT example compiling test)
[Paddle-TRT INT8 usage](#Paddle-TRT_INT8 usage)
[Paddle-TRT subgraph operation principle](#Paddle-TRT subgraph operation principle)
compile Paddle-TRT inference libraries¶
Use Docker to build inference libraries
TRT inference libraries can only be compiled using GPU.
Download Paddle
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.git
Get docker image
nvidia-docker run --name paddle_trt -v $PWD/Paddle:/Paddle -it hub.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddle:latest-dev /bin/bash
Build Paddle TensorRT
# perform the following operations in docker container cd /Paddle mkdir build cd build cmake .. \ -DWITH_FLUID_ONLY=ON \ -DWITH_MKL=OFF \ -DWITH_MKLDNN=OFF \ -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \ -DWITH_PYTHON=OFF \ -DTENSORRT_ROOT=/usr \ -DON_INFER=ON # build make -j # generate inference library make inference_lib_dist -j
Paddle-TRT interface usage¶
paddle_inference_api.h defines all APIs of TensorRT.
General steps are as follows:
Create appropriate AnalysisConfig.
Create
PaddlePredictorbased on config.Create input tensor.
Get output tensor and output result.
A complete process is shown below:
#include "paddle_inference_api.h"
namespace paddle {
using paddle::AnalysisConfig;
void RunTensorRT(int batch_size, std::string model_dirname) {
// 1. Create MixedRTConfig
AnalysisConfig config(model_dirname);
// config->SetModel(model_dirname + "/model",
// model_dirname + "/params");
config->EnableUseGpu(100, 0 /*gpu_id*/);
config->EnableTensorRtEngine(1 << 20 /*work_space_size*/, batch_size /*max_batch_size*/);
// 2. Create predictor based on config
auto predictor = CreatePaddlePredictor(config);
// 3. Create input tensor
int height = 224;
int width = 224;
float data[batch_size * 3 * height * width] = {0};
PaddleTensor tensor;
tensor.shape = std::vector<int>({batch_size, 3, height, width});
tensor.data = PaddleBuf(static_cast<void *>(data),
sizeof(float) * (batch_size * 3 * height * width));
tensor.dtype = PaddleDType::FLOAT32;
std::vector<PaddleTensor> paddle_tensor_feeds(1, tensor);
// 4. Create output tensor
std::vector<PaddleTensor> outputs;
// 5. Inference
predictor->Run(paddle_tensor_feeds, &outputs, batch_size);
const size_t num_elements = outputs.front().data.length() / sizeof(float);
auto *data = static_cast<float *>(outputs.front().data.data());
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_elements; i++) {
std::cout << "output: " << data[i] << std::endl;
}
}
} // namespace paddle
int main() {
// Download address of the model http://paddle-inference-dist.cdn.bcebos.com/tensorrt_test/mobilenet.tar.gz
paddle::RunTensorRT(1, "./mobilenet");
return 0;
}
The compilation process is here
Paddle-TRT INT8 usage¶
Paddle-TRT INT8 introduction
The parameters of the neural network are redundant to some extent. In many tasks, we can turn the Float32 model into Int8 model on the premise of precision. At present, Paddle-TRT supports to turn the trained Float32 model into Int8 model off line. The specific processes are as follows: 1)Create the calibration table. We prepare about 500 real input data, and input the data to the model. Paddle-TRT will count the range information of each op input and output value in the model, and record in the calibration table. The information can reduce the information loss during model transformation. 2)After creating the calibration table, run the model again, Paddle-TRT will load the calibration table automatically, and conduct the inference in the INT8 mode.compile and test the INT8 example
```shell
cd SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample
# sh run_impl.sh {the address of inference libraries} {the name of test script} {model directories}
# We generate 500 input data to simulate the process, and it's suggested that you use real example for experiment.
sh run_impl.sh BASE_DIR/fluid_inference_install_dir/ fluid_generate_calib_test SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1
```
After the running period, there will be a new file named trt_calib_* under the `SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/build/mobilenetv1` model directory, which is the calibration table.
``` shell
# conduct INT8 inference
# copy the model file with calibration tables to a specific address
cp -rf SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/build/mobilenetv1 SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1_calib
sh run_impl.sh BASE_DIR/fluid_inference_install_dir/ fluid_int8_test SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1_calib
```
Paddle-TRT subgraph operation principle¶
Subgraph is used to integrate TensorRT in PaddlePaddle. After model is loaded, neural network can be represented as a computing graph composed of variables and computing nodes. Functions Paddle TensorRT implements are to scan the whole picture, discover subgraphs that can be optimized with TensorRT and replace them with TensorRT nodes. During the inference of model, Paddle will call TensorRT library to optimize TensorRT nodes and call native library of Paddle to optimize other nodes. During the inference, TensorRT can integrate Op horizonally and vertically to filter redundant Ops and is able to choose appropriate kernel for specific Op in specific platform to speed up the inference of model.
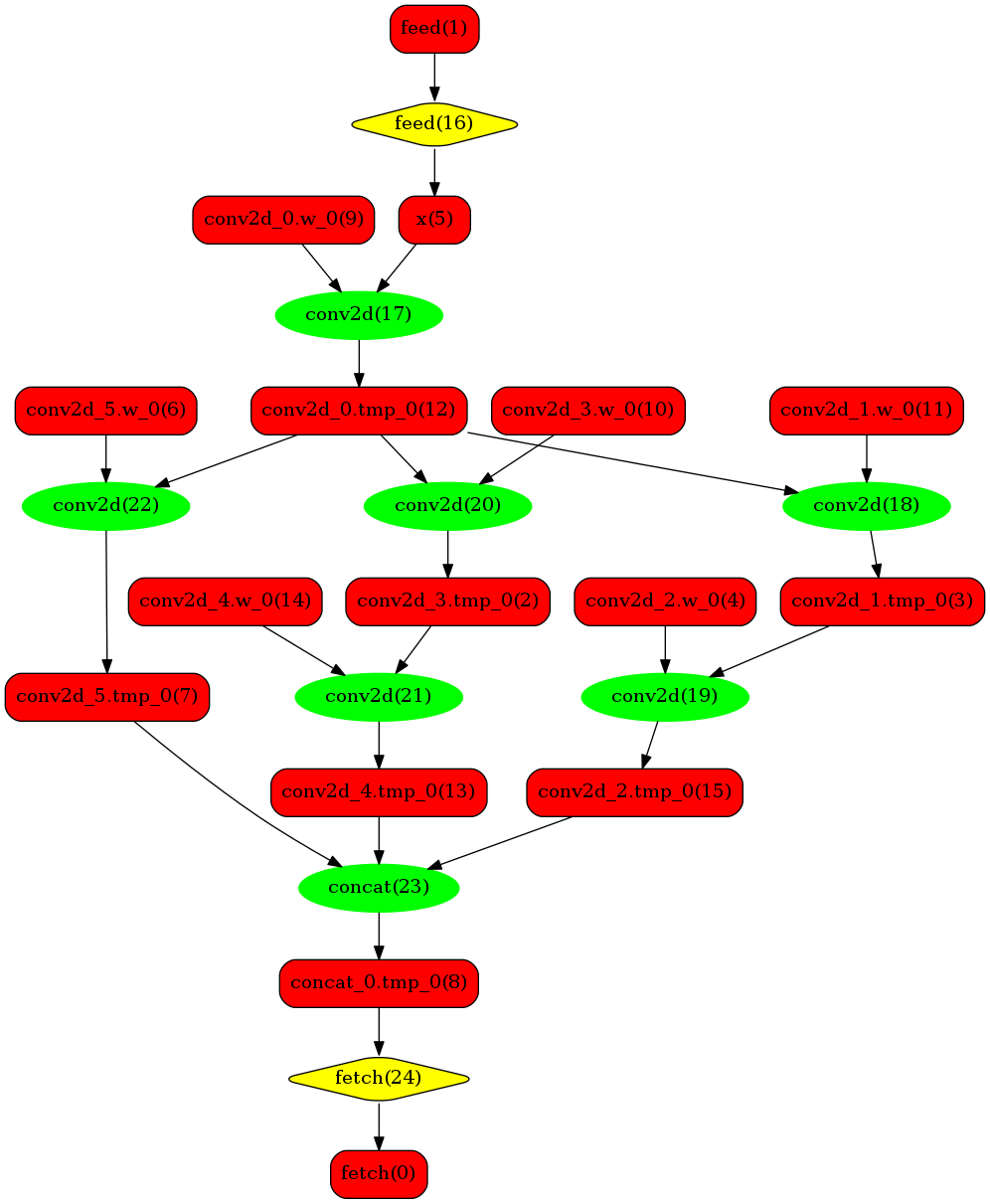
A simple model expresses the process :
Original Network
Transformed Network
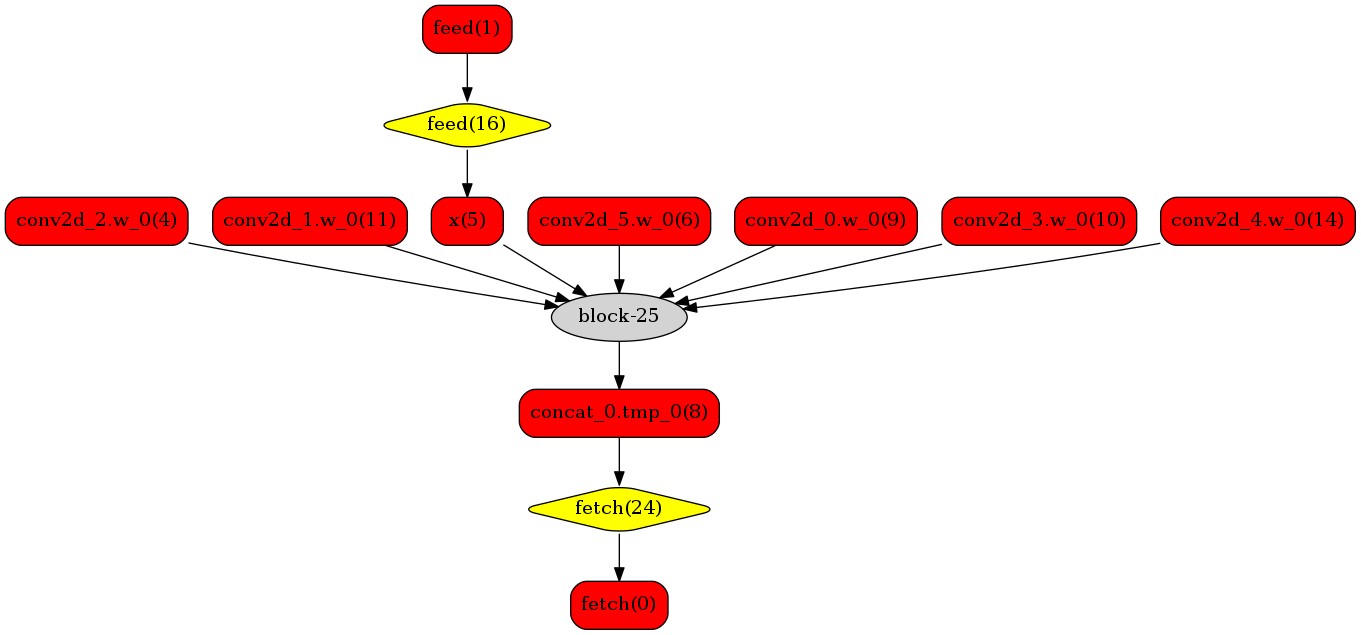
We can see in the Original Network that the green nodes represent nodes supported by TensorRT, the red nodes represent variables in network and yellow nodes represent nodes which can only be operated by native functions in Paddle. Green nodes in original network are extracted to compose subgraph which is replaced by a single TensorRT node to be transformed into block-25 node in network. When such nodes are encountered during the runtime, TensorRT library will be called to execute them.